Hearing and hearing problems
Instruction
In this topic you will learn about hearing and hearing problems in children.
How we hear
- Our ears collect sounds
- The sounds travel through the three parts of the ear
- The sounds are changed into electrical signals which are sent to the brain
- When the signals reach the brain, we hear the sounds and can recognize them.
To have good hearing, all parts of the ear must be working properly.
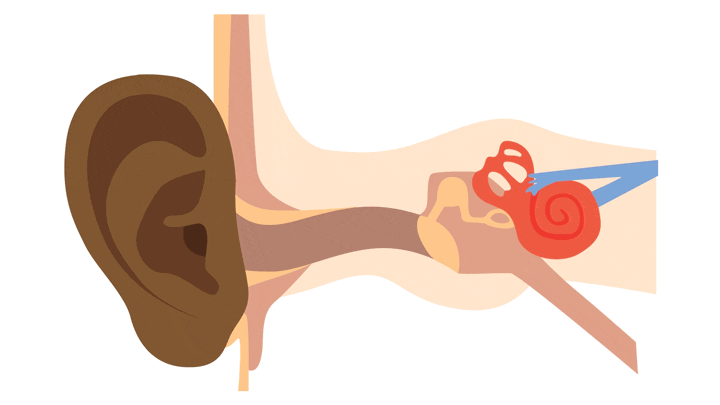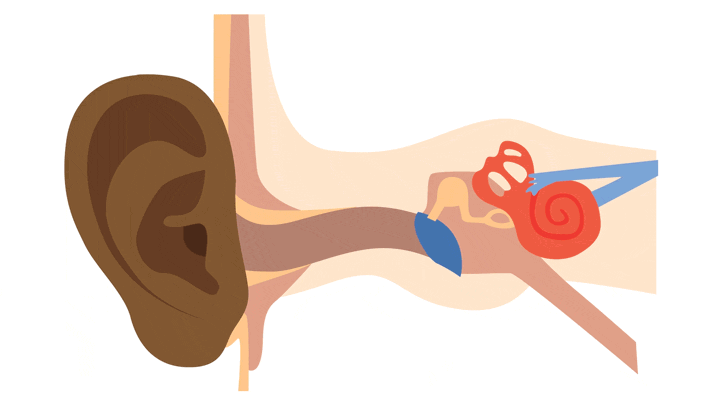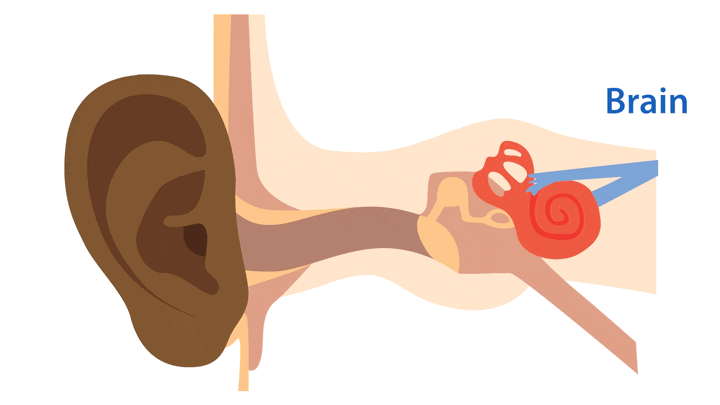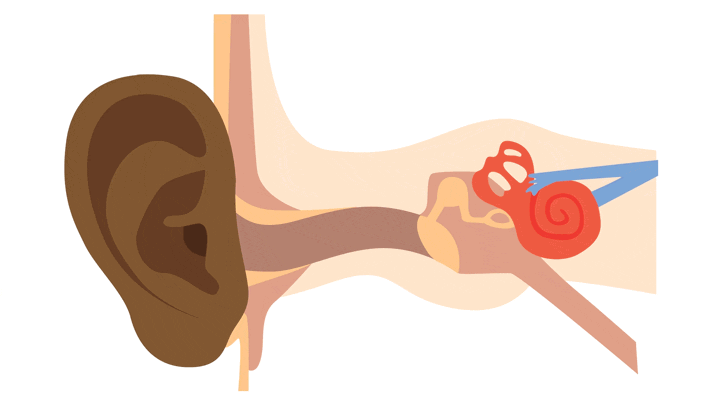
How sound travels through the ear
Hearing problems
People with hearing problems have difficulty hearing or recognizing sounds.
Activity
In pairs:
- One person blocks their ear on both sides with their finger or by using earplugs
- The other person uses their normal voice and tries to have a conversation.
This is how it feels to have mild to moderate hearing loss.
Mild to severe hearing loss
Hearing loss is also known as ‘hard of hearing’.
A child with mild, moderate or severe hearing loss cannot hear as well as other children.
They have difficulties with:
- Hearing what other people are saying in quiet and noisy environments
- Carrying out day-to-day tasks, including learning, without the help of assistive products such as hearing aids.
Meet Patryk

Patryk is six years old and goes to school. Patryk has repeated ear infections.
Patryk has difficulty hearing what people are saying when they are talking far away, or where there is background noise such as in a classroom.
Profound hearing loss
A child with profound hearing loss, in both ears, may have very little or no hearing. This is called ‘deafness’.
Prevention, treatment and assistance
Most hearing problems can be:
- Prevented. For example, wearing earplugs in noisy places
- Treated. For example, receiving medication for ear health problems
- Helped. For example, through assistive products and/or rehabilitation.
Meet Garret

Garret is 9 years old and lives in a fishing village. He likes diving in the sea with his friends. Garret has frequent pain and discharge from his ears.
During sensory screening at his school, the screener found that Garret had ear health problems.
He was referred to local ear care personnel and received treatment for his ear infection.
Question
Which of the following is an example of preventing hearing problems?
Select one.
If you selected b, you are correct!
Avoiding loud noise is an important way to prevent damage to a child’s hearing.
a, c, and d are incorrect.
These do not prevent hearing problems. Treatment is used for existing health problems. Assistive products and rehabilitation assist a person with hearing loss to participate and be included in activities.
Discussion
Discuss with colleagues:
- Do you or does anyone you know wear hearing aids?
- What would be the effect on a child who needs hearing aids but does not have access to them?
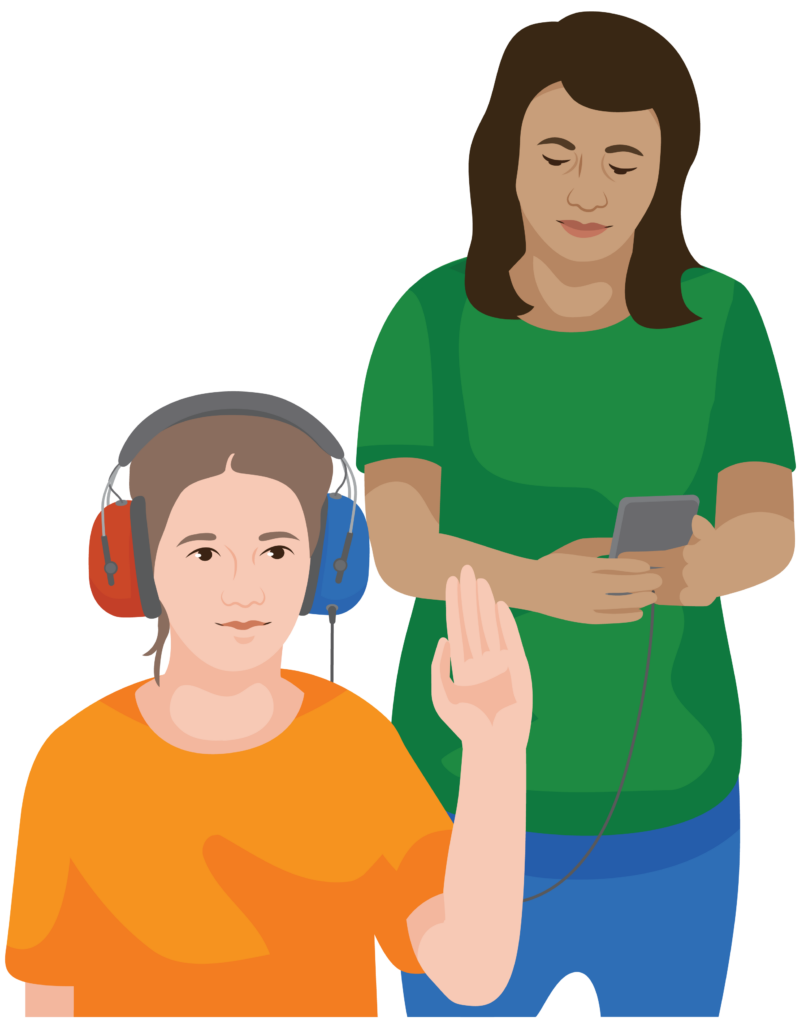

How is hearing screened?
Hearing is screened using audiometry.
This involves the child listening to sounds through headphones and indicating which ones they can hear.
The sounds are produced by an audiometer. For example, a digital tablet or a smartphone loaded with a hearing screen app.
Instruction
Learn how to use audiometry for a hearing screen, in Lesson four.
Different types of sound are presented to a person’s ear at different frequencies.
For example, a male voice typically has a lower frequency sound than a female voice.
The frequency of sound is measured in Hertz (Hz).