Assistive products and how they support people
Assistive products support people in many ways. The right assistive product can support a person to:
- Be included and participate in what that they want or need to do
- Be more independent and have less need of caregiver support
- Have better health and wellbeing
Watch the videos to find out how assistive products can support people in their daily lives.
Reflection
- What types of assistive products did you see people using in the videos?
- What difference do the assistive products make in their lives?
There are many different types of assistive products. Through each of the TAP modules, you can learn about some of the assistive products that are included in the WHO Priority Assistive Products List.
This includes assistive products that can help with:
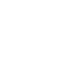
- Cognition (thinking) – such as pill organisers and whiteboards to remember things
Pill organiser

Whiteboard
- Communication – such as communication boards, books, and cards

Communication board
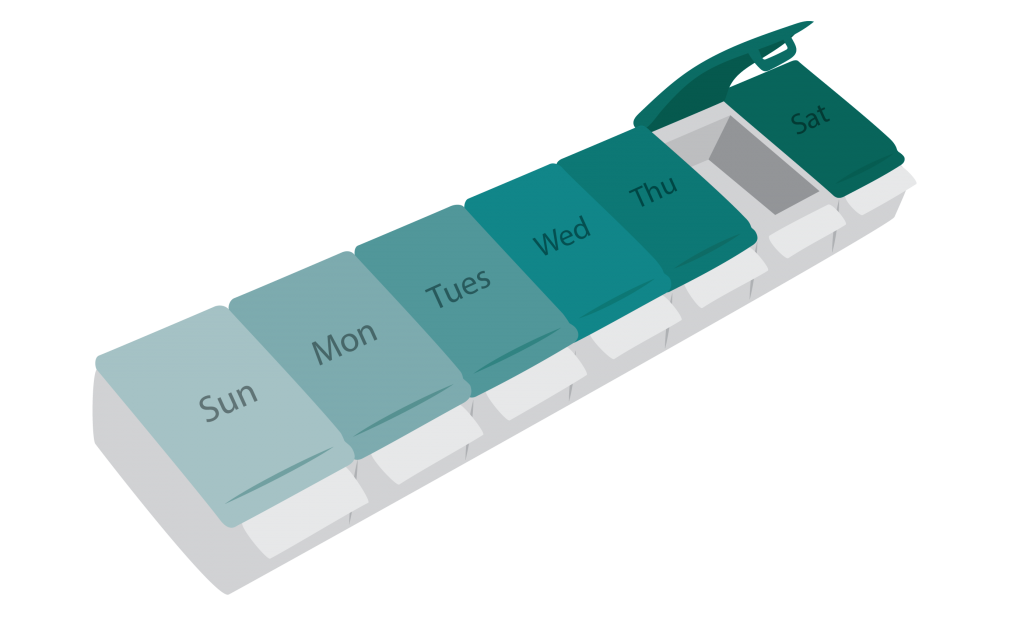
- Hearing – such as hearing aids and alarm signallers that use light, sound, and vibration
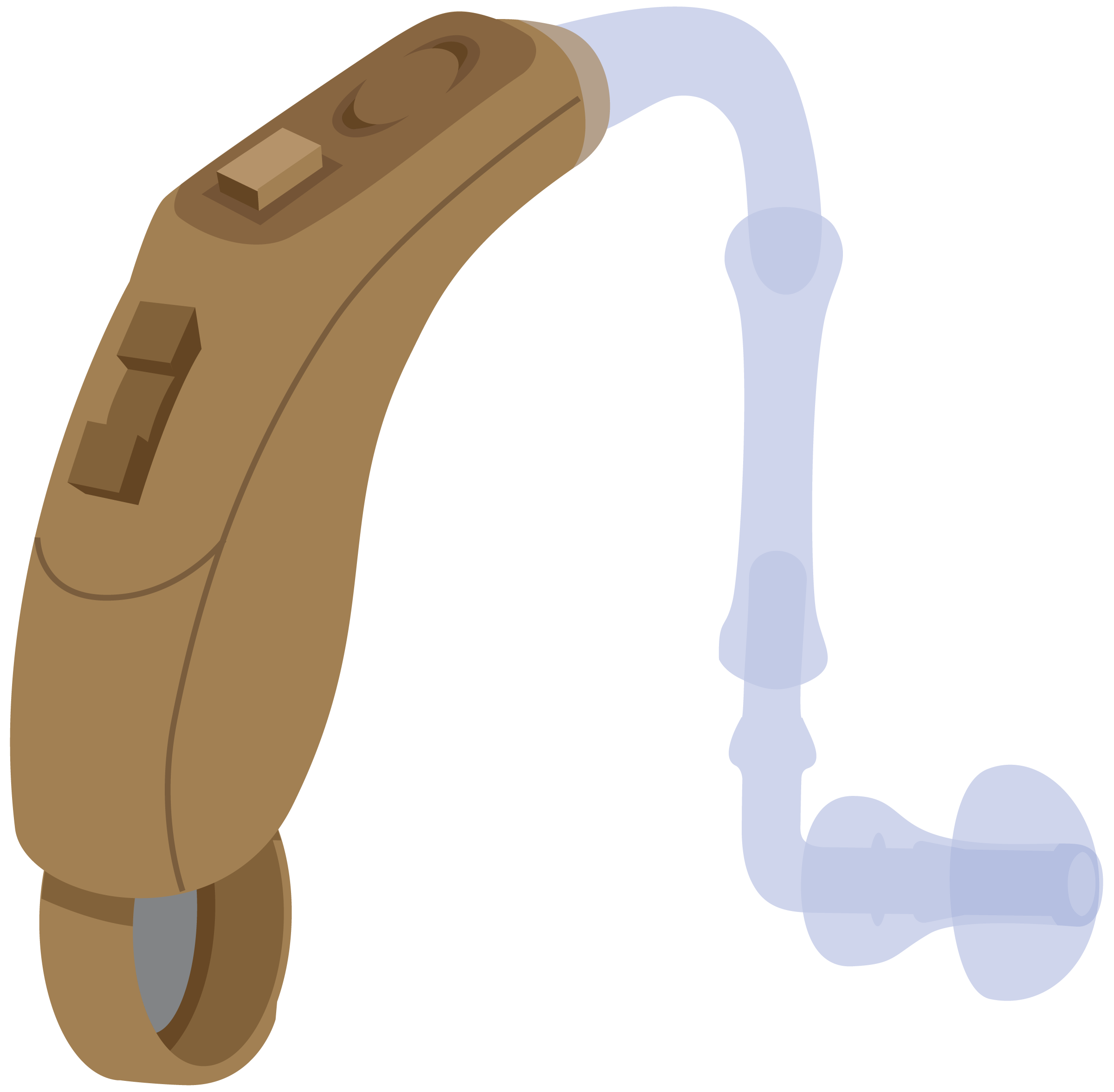

Hearing aid
Alarm signaller
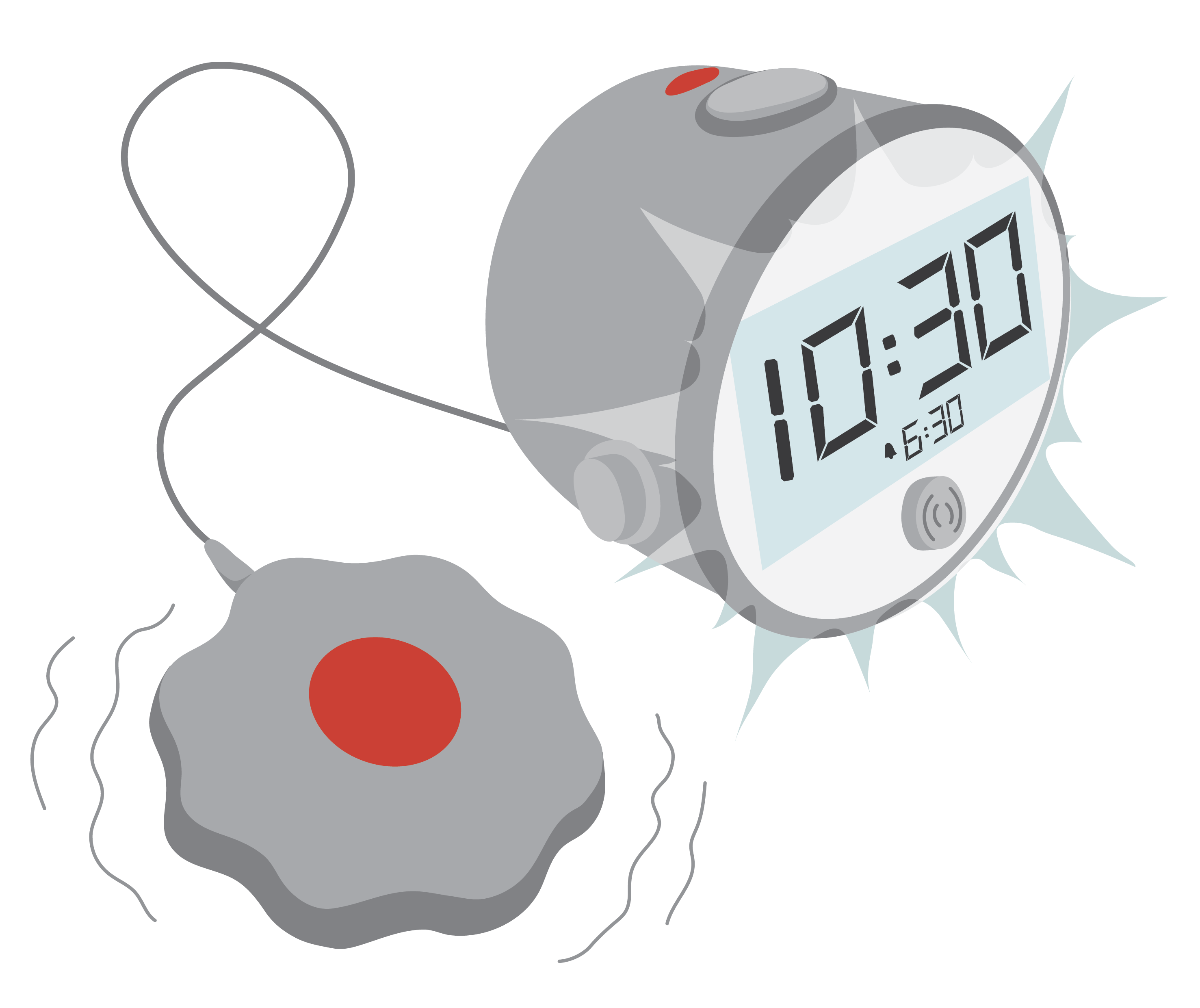
- Mobility (moving about) – such as walking aids, portable ramps, and grab bars
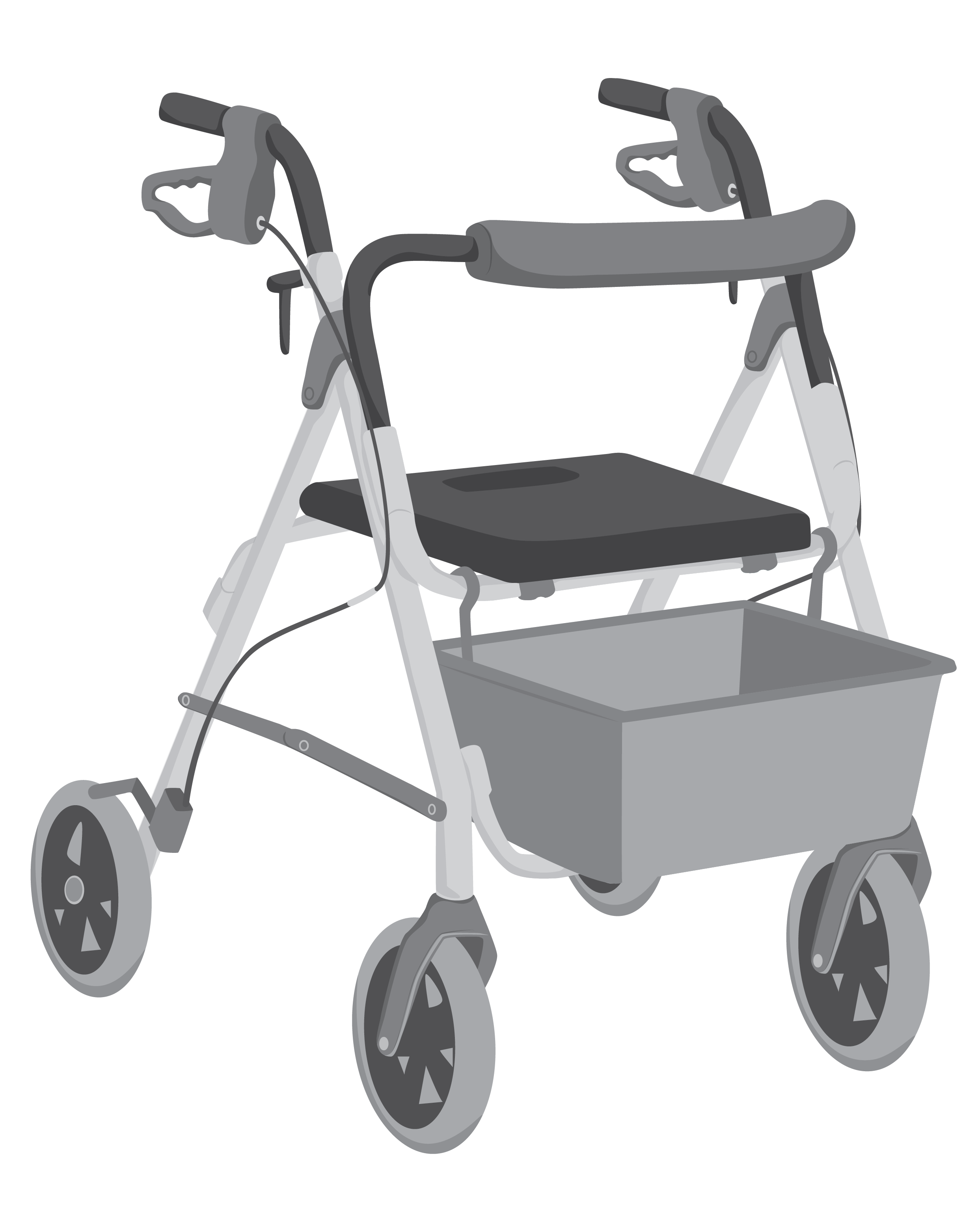

Rollator
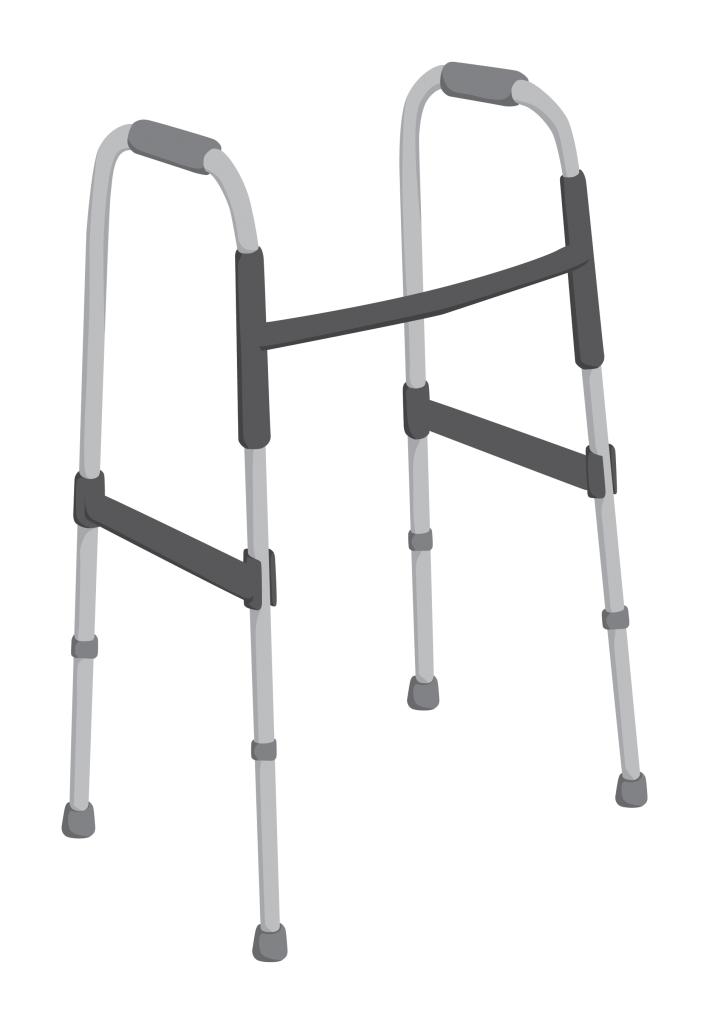

Walking frame

Grab bar
Portable ramp
- Self-care – such as toilet and shower chairs, absorbent cloths, and catheters

Toilet chair

Absorbent cloth

Nelaton catheter
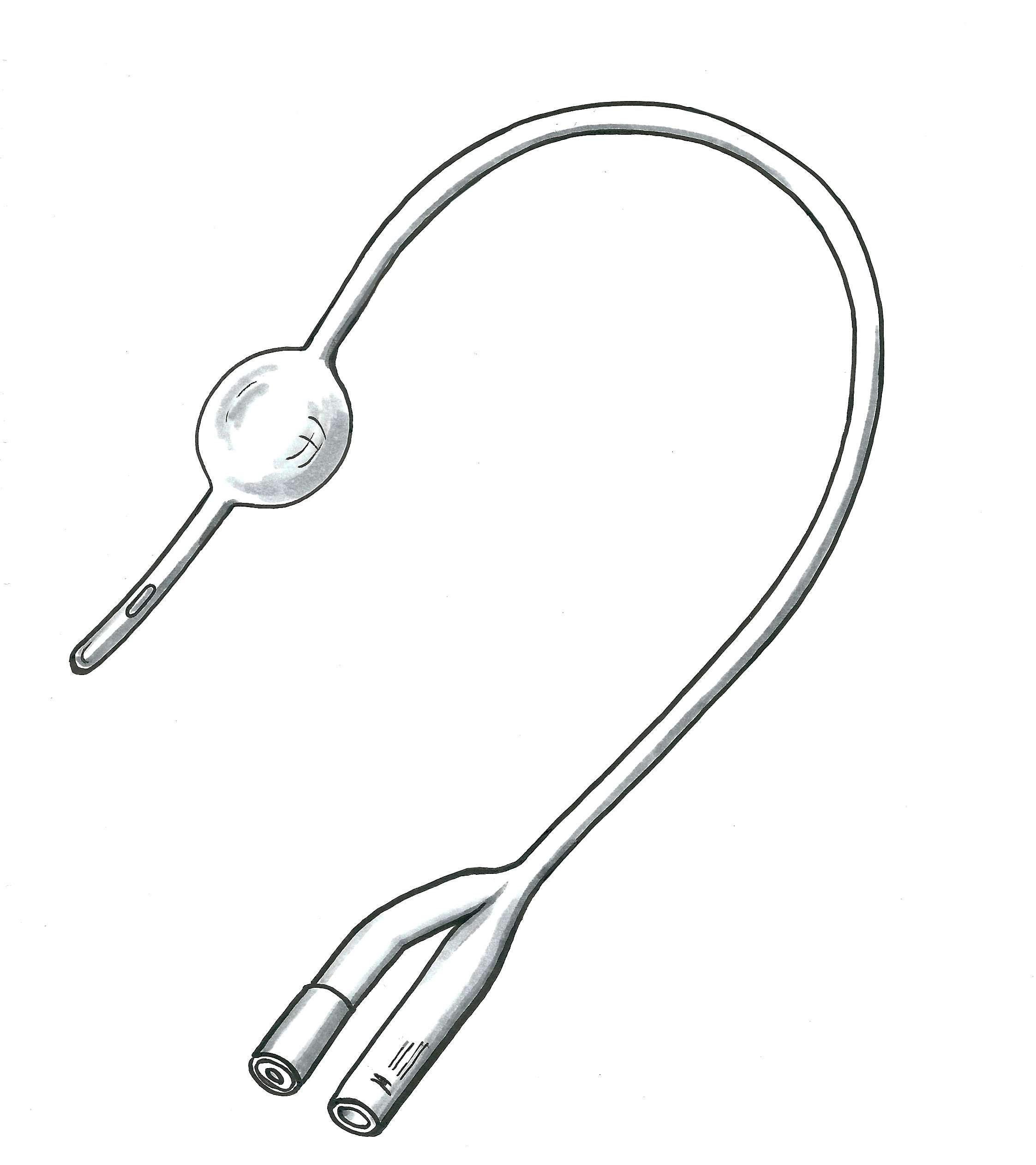
Foley catheter
- Vision (seeing) – such as reading glasses, magnifiers, audio players, talking and/or touching watches, and white canes

Reading glasses

Handheld magnifier
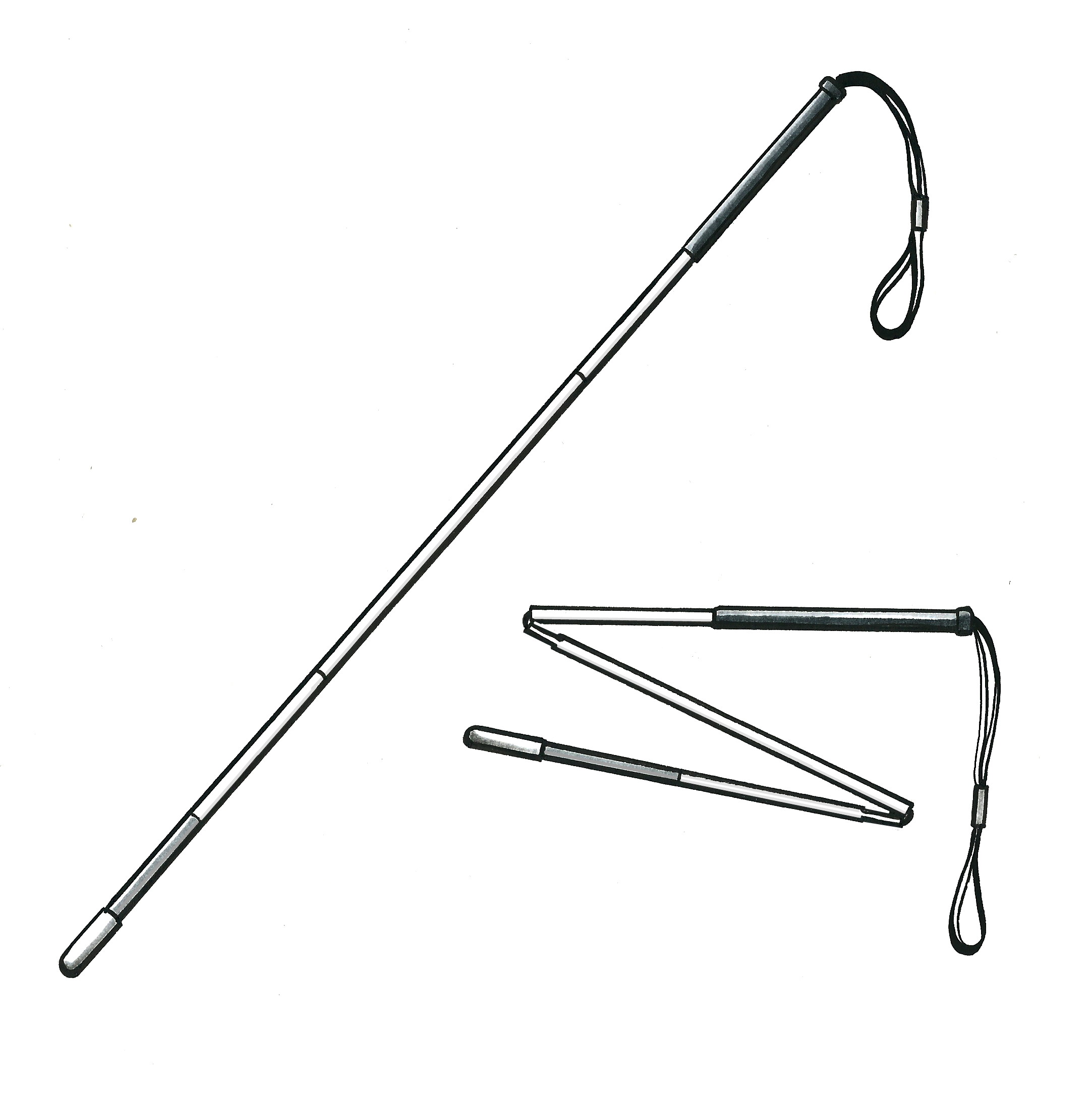
White cane

Talking and/or touching watch
Often there is a range (more than one type) of the same assistive product.
For example:
- Walking aids include elbow crutches, underarm crutches, walking frames, and walking sticks.
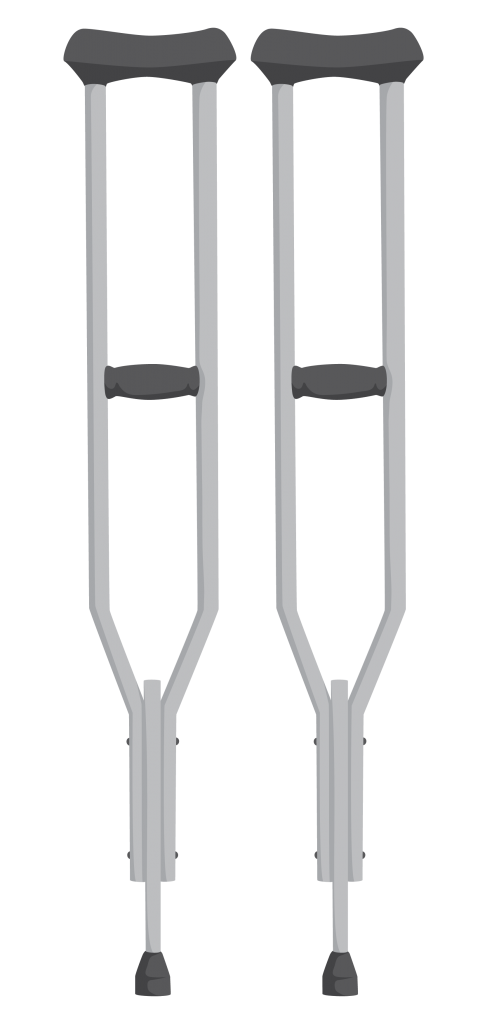
Axilla crutches
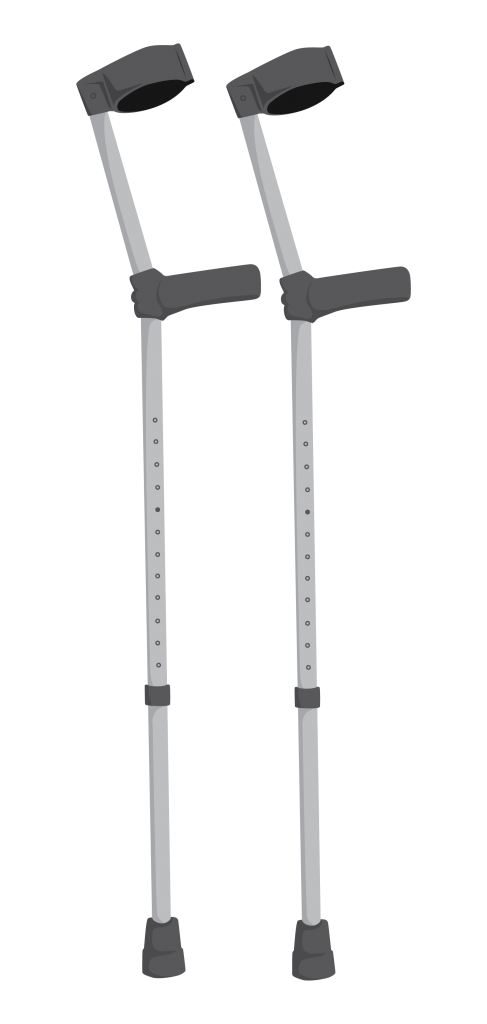
Elbow crutches

Rollator

Walking stick
- Magnifiers include hand held magnifiers (such as pocket magnifiers), stand magnifiers, and spectacle magnifiers.

Handheld magnifier

Pocket magnifier
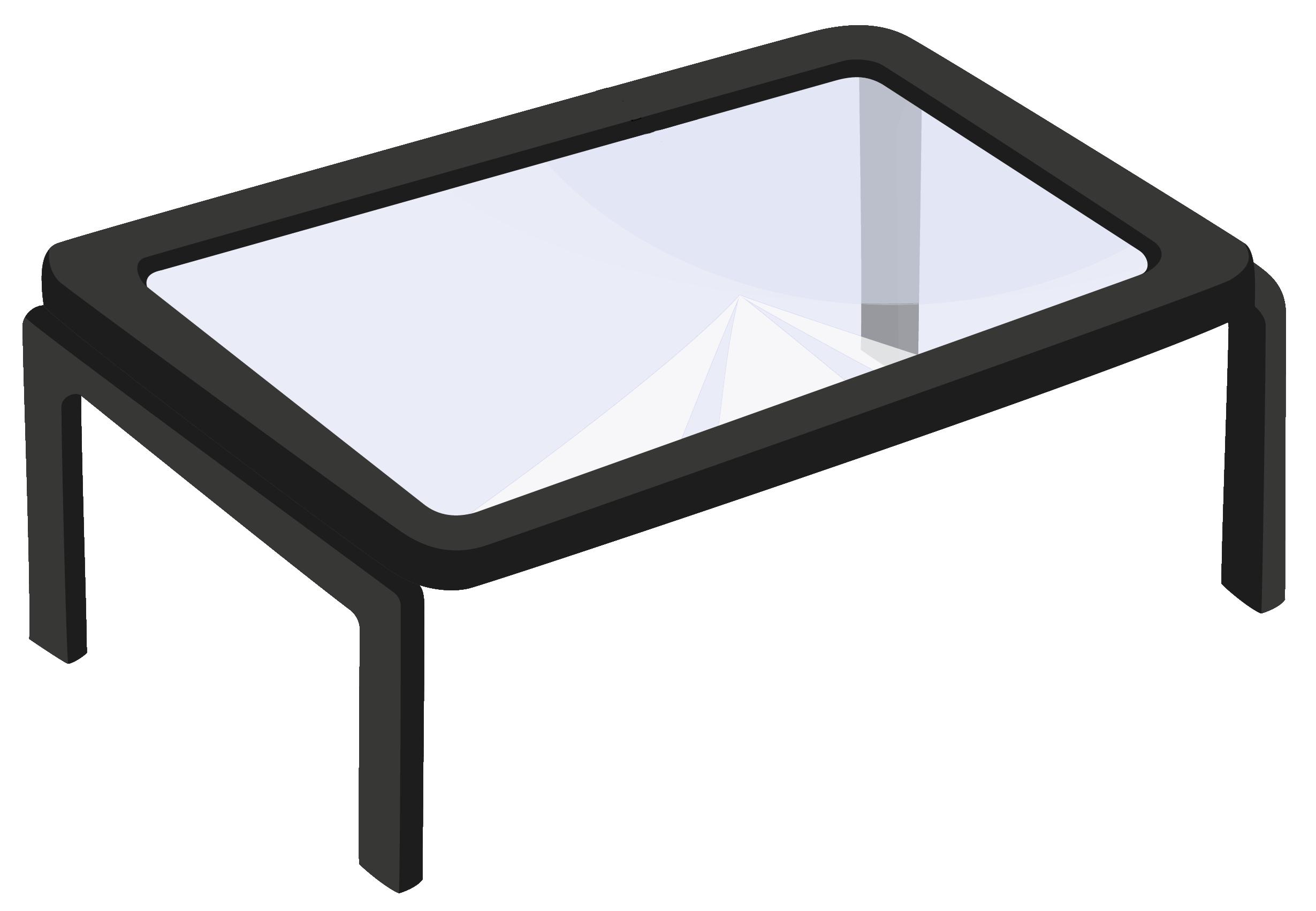
Stand magnifier
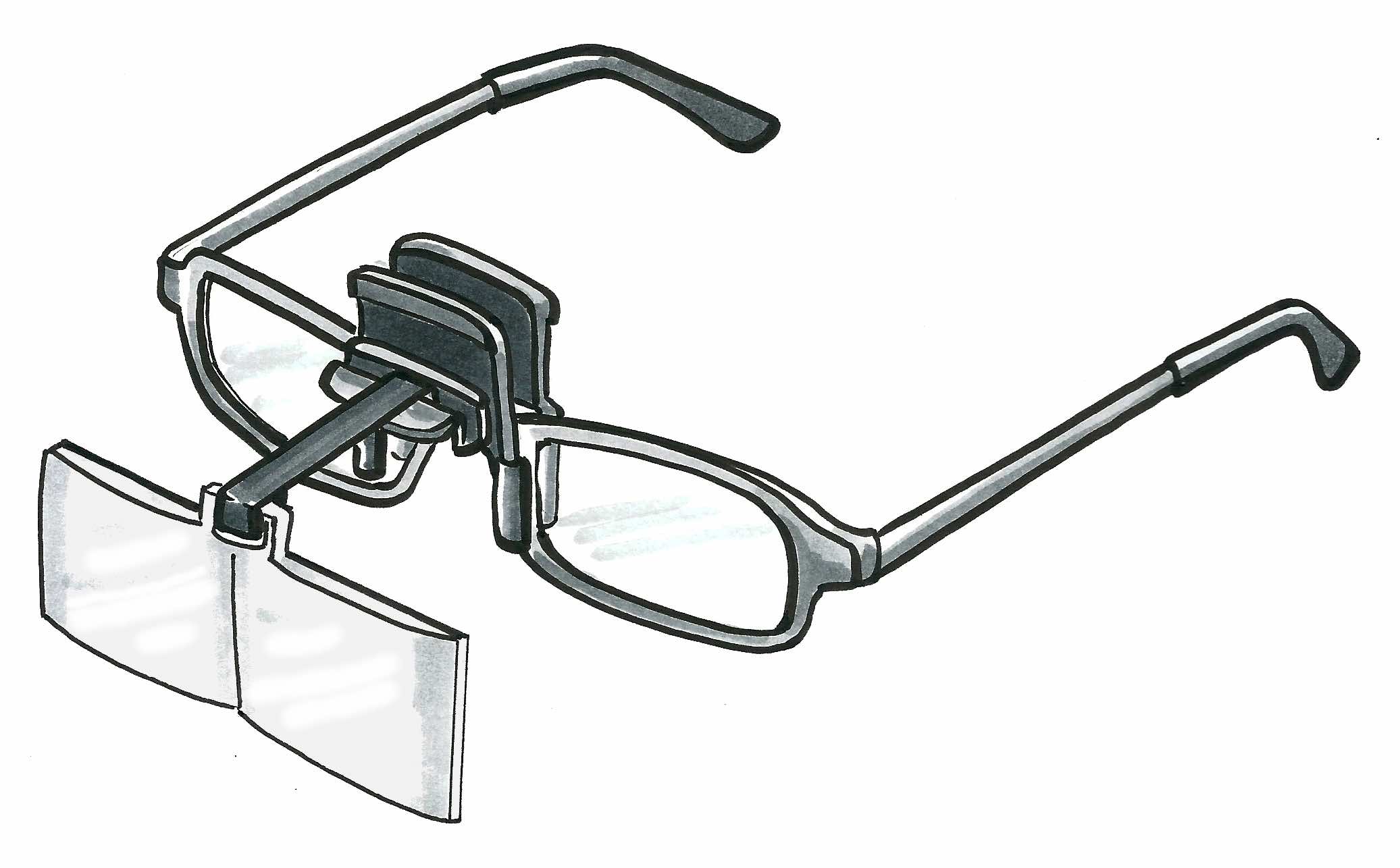
Spectacle magnifier
Discussion
Do you have examples of how any of the assistive products introduced in this topic have helped you or people that you know?
What about other assistive products?
Share examples with each other if you are in a group.